Navy Blue Classic Peacoat Womans Wool Cracker Jack
Today, we continue our overcoat series with the iconic Peacoat. We will explore the history of this classic garment and detail how to find the right cut, fabric, and buttons so you can make an informed decision about your own peacoat purchase.
The History of the Peacoat
Unlike the more defined history of the Trench Coat, the origins of the peacoat are more ambiguous. A version of the jacket has been worn by European and American sailors for nearly three centuries, so it's probably not surprising that there are several differing versions of the peacoat story out there. Let's look at them one by one. Like many garments, the history of the peacoat may not be exact, but it has certainly left an indelible impression upon classic fashion.

Peacoat Origins Story #1: The Dutch Version
The Oxford Dictionary dates the origin of the term pea jacket or peacoat to the early 18th century, claiming that it was most likely derived from the Dutch word pijjakker, from "pij" for 'coat of coarse cloth' +jekker for 'jacket'. Since the Dutch were a naval power for many centuries, and the peacoat is commonly associated with seafaring, it does not seem far-fetched that the jacket was in fact from the Netherlands.

Peacoat Origins Story #2: The Camplin Version
According to Camplin, a heritage British clothing brand that is now based in Italy, Mr. Edgard Camplin founded a store in 1850 in which he sold uniforms to the British navy. Apparently, he sold particularly well in India, starting in 1888. After that, Mr. Camplin supposedly suggested – at an unknown date – to create a coat for the uniform of petty officers, who had the same uniform as sailors up until then. Instead of the officer's greatcoat, the Camplin designed the Petty Coat, which was also known as a P. Coat. The name eventually was popularized as Peacoat for phonetic reasons. This version of the story may be true, but it does not name any sources or dates other than the company's own records; the company still sells peacoats based on the story that Mr. Edgard Camplin "invented" the peacoat.
Peacoat Origins Story #3: The Tailor & Cutter Version
The Tailor & Cutter used to be the leading tailor trade magazine in England in the 19th century. It was published weekly and in addition to focusing on tailoring and cutting, it also featured fashion trends and etiquette. For example, if people began wearing new styles, Tailor & Cutter would comment on the clothing, which was particularly true for anything a Royal wore. In an issue from October 1868, they report about the so-called "the Prince of Wales Jacket" emerged, which characterized it as a loose double breasted jacket with three pairs of buttons, two cross pockets, and wide piping.
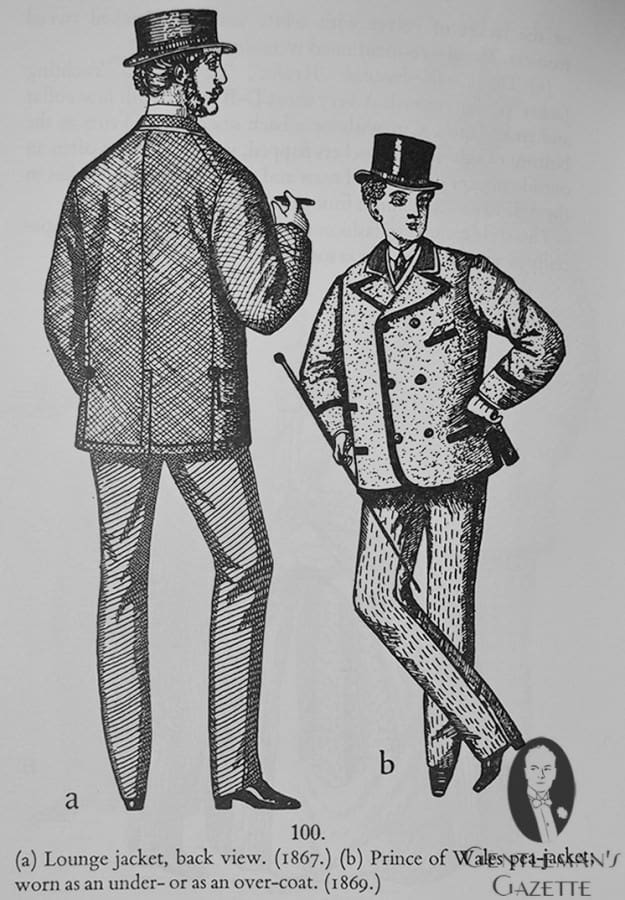
When intended for rough use, the coat was made of blue pilot-cloth lined with wool. For town wear, it was made of blue witney or another soft material with silk-faced lapels and a velvet collar. It was tailored with or without a back-seam and with short vents at the bottom. The illustration is from 1869 and describes it as a "Prince of Wales pea-jacket". Chances are, the PoW was not the inventor, but rather he was the person who popularized it.
What is a Peacoat?
All these historic details now beg the question: what is a peacoat today? Let's take a look at the three major components of a peacoat's construction: the cut, the fabric, and the buttons.
The Cut of a Peacoat
The peacoat of today has a specific cut that reflects it's functional origins. The peacoat is a simple jacket with a straight cut down the body. The length is slightly longer than a regular jacket, but it remains shorter than an overcoat like its predecessor.
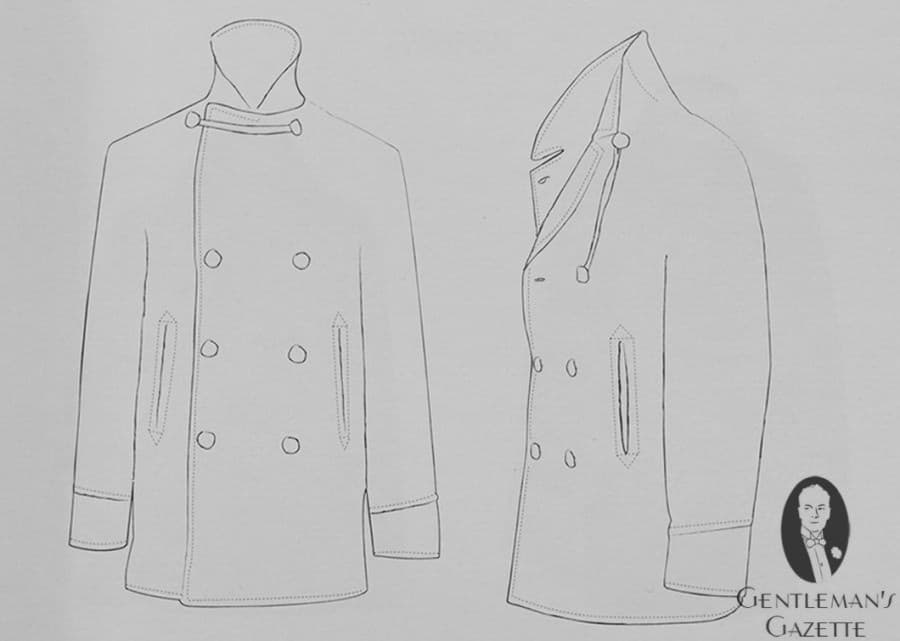

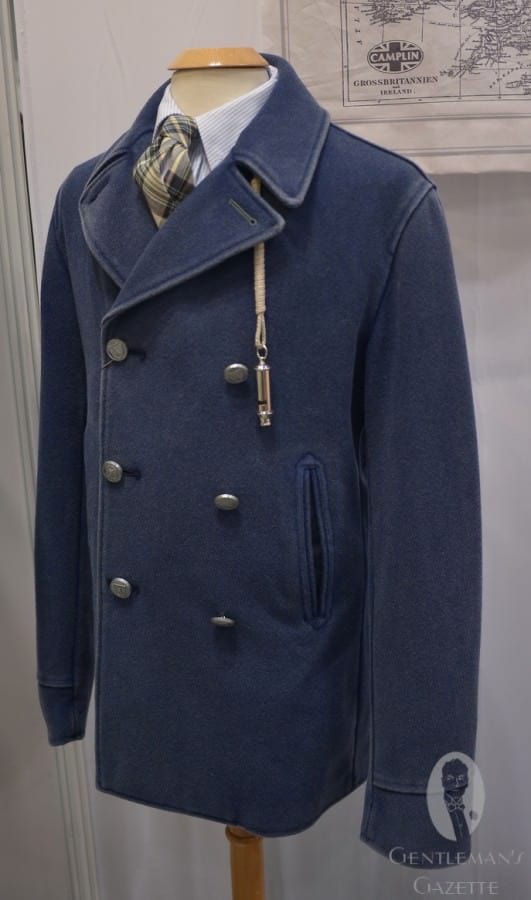
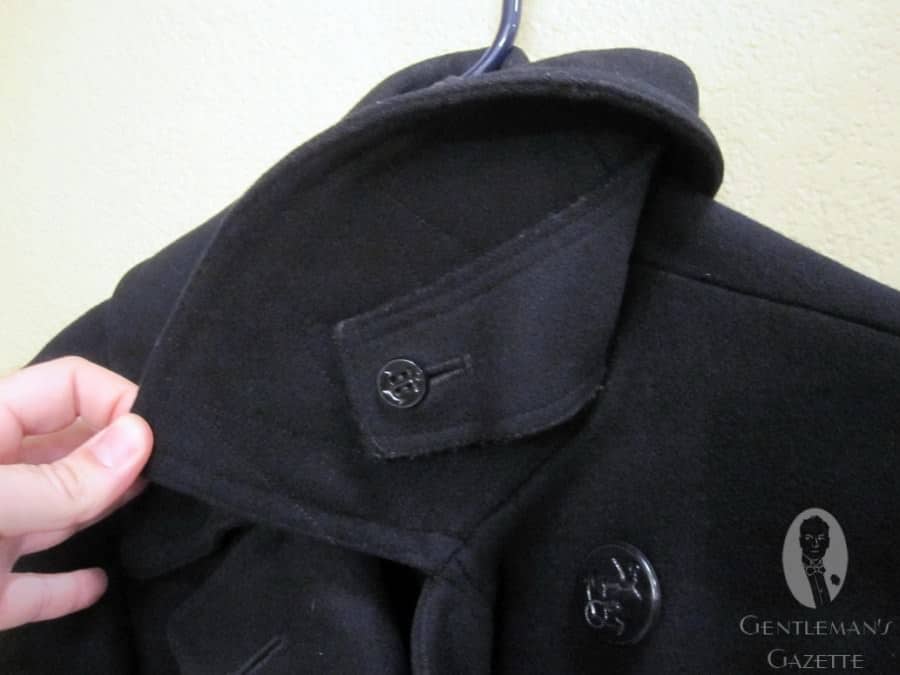
An oversized Ulster collar allows the wearer to button up the collar around the face for extra protection from the elements, using the 7th button (and occasionally the cordage, depending on the brand). If sailors wore many layers underneath, they were sometimes unable to button that 7th button and so they used cordage. The remaining 6 buttons are arranged traditionally on the double-breasted silhouette.

The very first peacoats seem to have had short side vents or no vents, whereas current US Navy peacoats feature a center vent. The vertical slit pockets were designed for easy access, and they usually also feature a little change pocket on the inside because US Navy pants did not have pockets. On the inside, you will find two pockets on either side for storage of your everyday carry items.
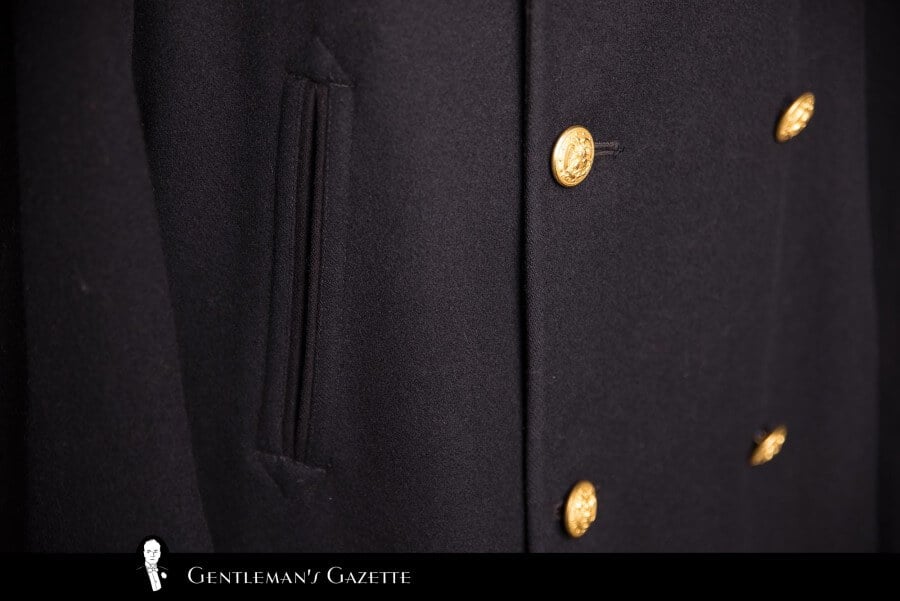

Aside from these simple details, the peacoat features no additional ornamentation, but it's simplicity and clean lines have made it a reliable standard for a classic wardrobe.
Today, the US Navy provides the features of a peacoat: "A double-breasted, hip-length coat made of dark blue authorized fabric with a convertible collar, a set-in pocket in each forefront, and a single row of four 35-line plack plastic anchor buttons down the right front and three on the left."
The correct wear is specified as: "Button all buttons except collar button. The collar button may be buttoned in inclement weather. Wear the jumper collar inside the coat. Sleeves are to reach about three-quarters of the distance from the wrist to the knuckles when arms hang naturally at the sides."
Peacoat Fabric
Today, the US Navy peacoat is made of a midnight blue 24 oz / 750 grams Melton of 80% wool and 20% artificial fibers. Traditionally, it was made of 100% Kersey wool, just like the Melton for the British Warm. As pointed out above, the pilot fabric was an option and later 100% wool Melton or Kersey was used, often in weights up to 34 oz. / 1050 / grams per yard / meter. Today, you can still find 100% wool melton fabrics, but usually not heavier than 24 oz, which is a shame because the heavier fabrics wear quite warm. If you can, get a heavy weight vintage coat, though good examples in decent shape are few and far between. If you opt for a modern version, skip the nylon and polyester blends and invest a bit more.
Occasionally, you will also find peacoats made in different materials such as canvas, cotton or nylon, but technically, these are not peacoats.
Buttons of a Peacoat
Throughout history, peacoats had a varying number of front buttons. During WWI they often had 10 buttons, later 8 and now mostly 6 with one hidden button under the right collar.
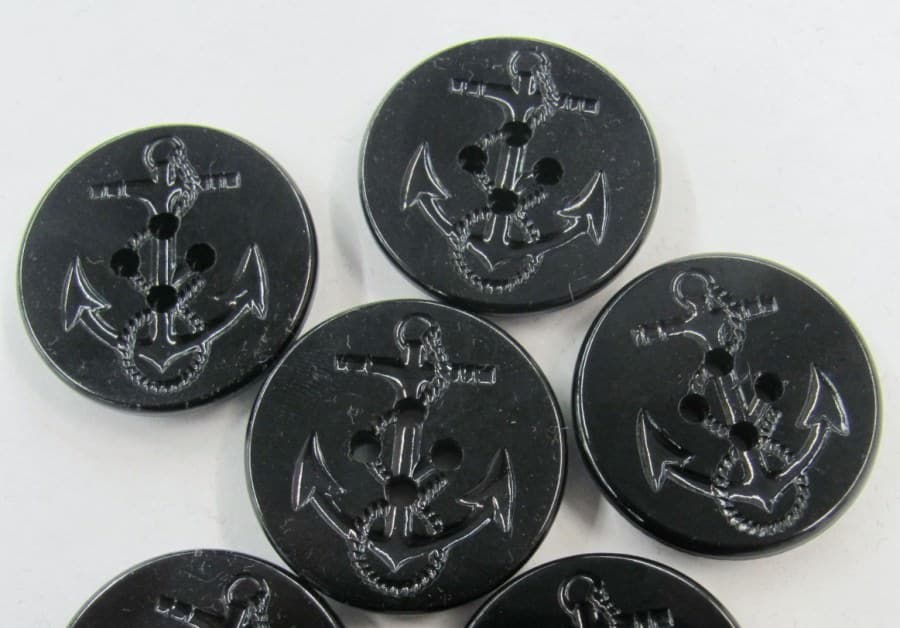
Today, US Navy peacoats feature large (35-ligne) thick black plastic buttons. Imprinted on the front is a "fouled anchor" design, which refers to the traditional image of an anchor wrapped in a rope. Apparently, the tradition of this logo dates back to the personal seal of Lord Howard of Effingham, the Lord High Admiral of England, when the British defeated the Spanish Armada in 1588. Following the victory, the design was then adopted as the official seal of the Lord High Admiral of Great Britain.

Every once in a while, you will also see gold brass buttons on a midnight blue peacoat. Traditionally, officers, warrant officers or chief petty officers could upgrade their peacoats with these buttons.
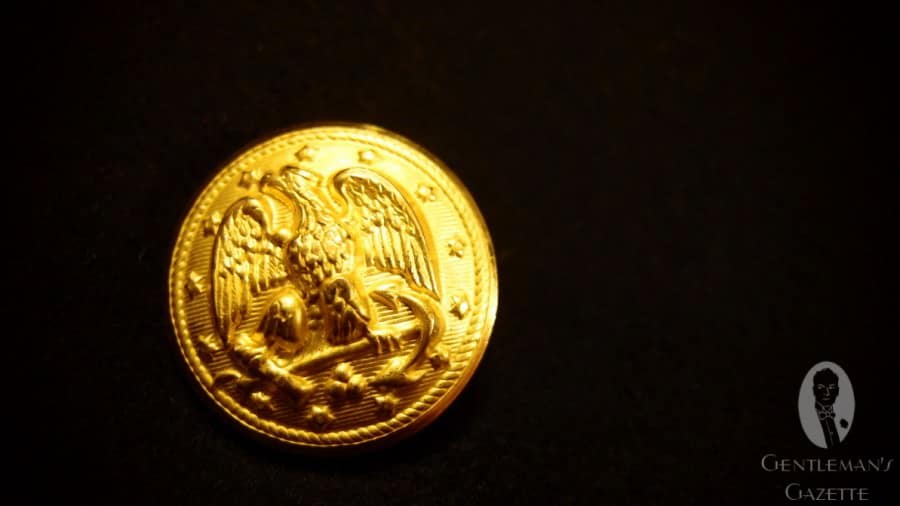

Starting in the early 20th century, peacoat buttons featured the large fouled anchor in the center with a ring of 13 stars surrounding it, spaced along the edge of the button face. At that time, the coat was also longer and had two additional horizontal pockets.
By the 1920s, peacoats had the buttons that are used today, but in the 1970's Admiral Elmo Zumwalt had these buttons replaced with 40-ligne (1″) metal buttons that looked identical to the gold ones worn by officers, with the exception that they had a pewter color.

The pewter "Zumwalt" buttons do have an anchor in the design, but only as a perch for a large eagle; they also feature a small stack of cannonballs. In 1984, the pewter buttons disappeared again, and "traditional" fouled anchor buttons returned.
While variants of the peacoat are used by many navies, and most use buttons with some variant of the fouled anchor design (with a crown, if the country is a kingdom), it is also true that many of these buttons are of brass, gold plated or not; or of anodized aluminum ("Stabrite"). Sometimes the buttons are of black plastic or horn, but with metal shanks rather than four holes for sewing.
Some will argue that an authentic US Navy peacoat must have the black anchor plastic buttons, but you should bear in mind that as a civilian, you can wear whatever you want. For example, I think it looks great with gold buttons, pewter buttons, horn buttons or mother of pearl buttons. It's nice to add a bit of contrast to an otherwise very simple jacket.
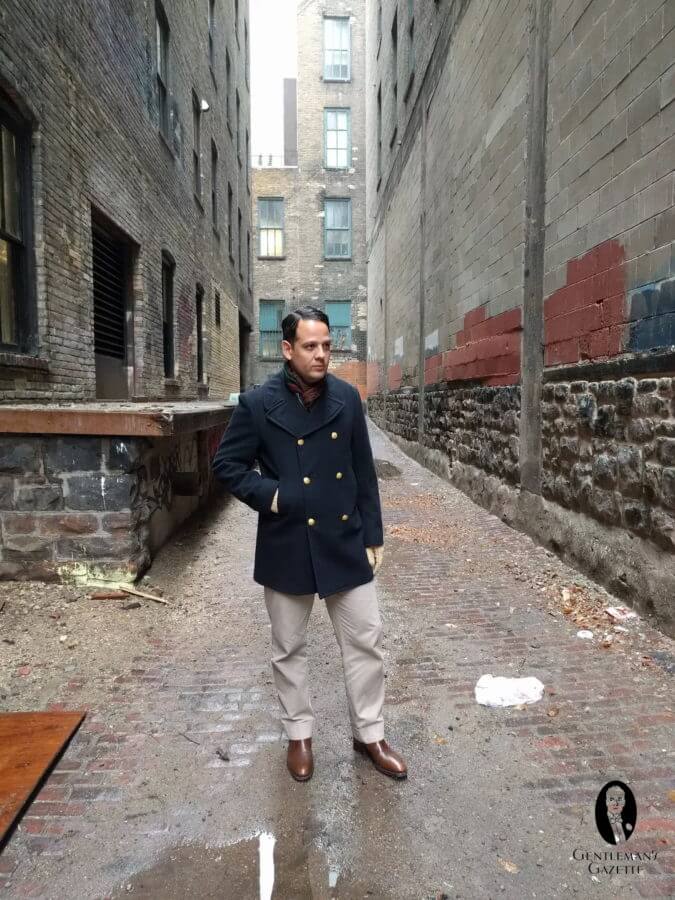

Personally, I have an original US Navy 100% wool officer's peacoat with gold buttons from the 1980's.
Where & How to Buy a Peacoat
If you want to buy a US Navy Peacoat, you can either buy a new one or a vintage one. Unfortunately, the Navy stopped issuing peacoats in May 2019, so new-old stock is the only remaining option if you want an unworn US Navy issue peacoat.
Recent peacoats are thinner due to the nylon blended into the fabric, while older versions in good shape are not easy to find. But no matter what you buy, the sizing has to be right to look good.

Peacoat Sizing
Traditionally peacoats are worn fitted, but not so tight that the vent gaps or you have wrinkles when buttoning the coat. To find the right size for you, you have to determine how you like the fit of your peacoat and physically measure your chest with a measuring tape.

For example, my chest is 44 inches, and I wear a 42L peacoat, which measures 45 inches in the chest. I am 6 ft tall with long arms, which is why I opted for the long version rather than the regular model. I do have enough space to wear a thick sweater or even a jacket underneath of it. In case you want to wear less, you should size down by more than two inches. If you like it roomier, size up.
Vintage Peacoat Sizing
Older peacoats were generally cut a little trimmer. Coats from around World War II were the most fitted ones.
The models from the 1950's and 1960's were already a littler bigger, and the 1970's version is once again bigger but a bit slimmer than the 1980's versions. The current model is cut the widest. With a WWII coat, a 44L would probably be as wide as 1980's 42 L.
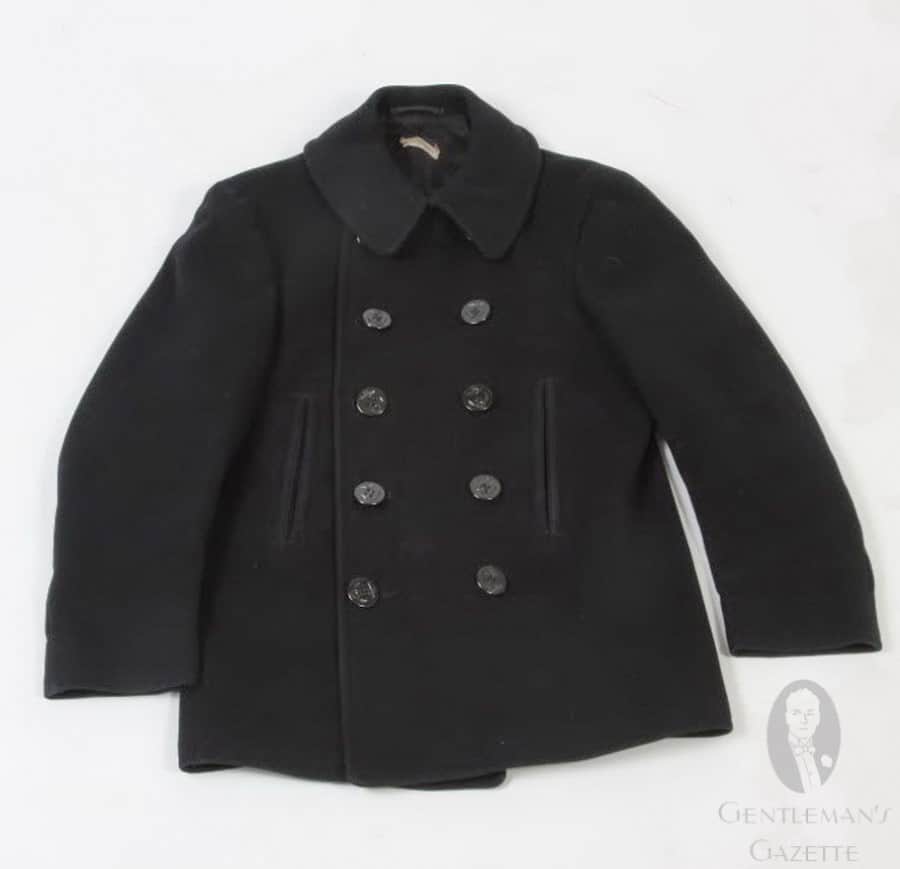

Sometimes, older coats do not have size measurements and in general, I would always go with measurements instead of sizes. Back length, sleeve length, shoulder width and chest width and maybe the waist should be enough to determine whether it will fit or not. Of course, if you have sloping shoulders or a round back it may not fit you, but an alterations tailor should be able to help you if these primary measurements are correct.

Sources for Vintage Coats
Ebay probably offers the largest selection of vintage peacoats, but if you live in the US, consignment stores may also offer one every once in a while. I put together a collection of 60+ peacoats here so take a look.
Sources for New Peacoats
There are some other clothing companies that offer peacoats, but most have added their own design elements.
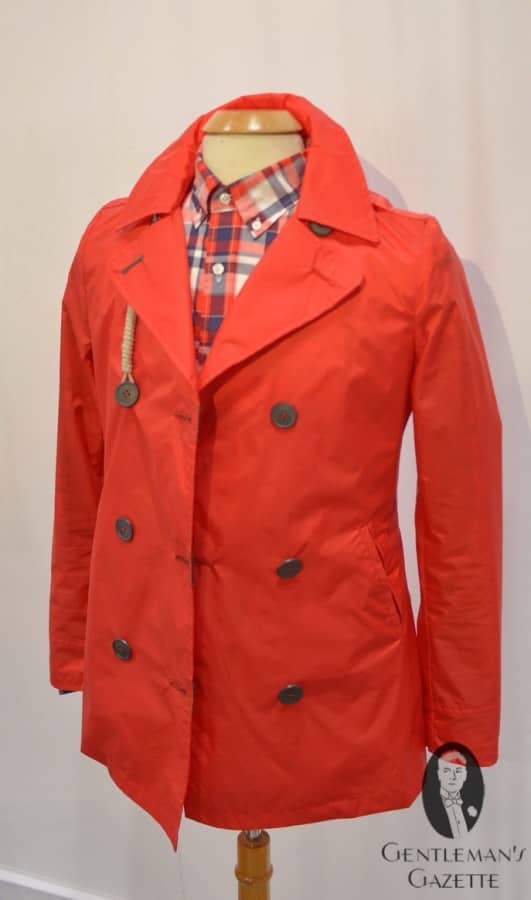

If you are not concerned about strict authenticity, the peacoat from Camplin (now Italian-owned) may be the right choice for you. They come in various colors, but they also cost two and a half times as much as the US-made ones.
Army-Navy surplus stores are likely to have the modern wool-synthetic blends; online surplus stores like this one also carry a variety of peacoats. While these are very affordable, and they come in thick 32 oz melton fabric, they are made out of reprocessed wool and nylon fibers, with polyester padding and quilted nylon lining, which is simply unacceptable to me.
Of course, all the fashion brands like Burberry and Aquascutum carry what they call Pea Coats but they are not the real deal. Even houses like Gieves & Hawkes only offer Made in Italy interpretations of the original with flap pockets and cashmere blends… If you like the look of these coats, wear them but these are not peacoats.
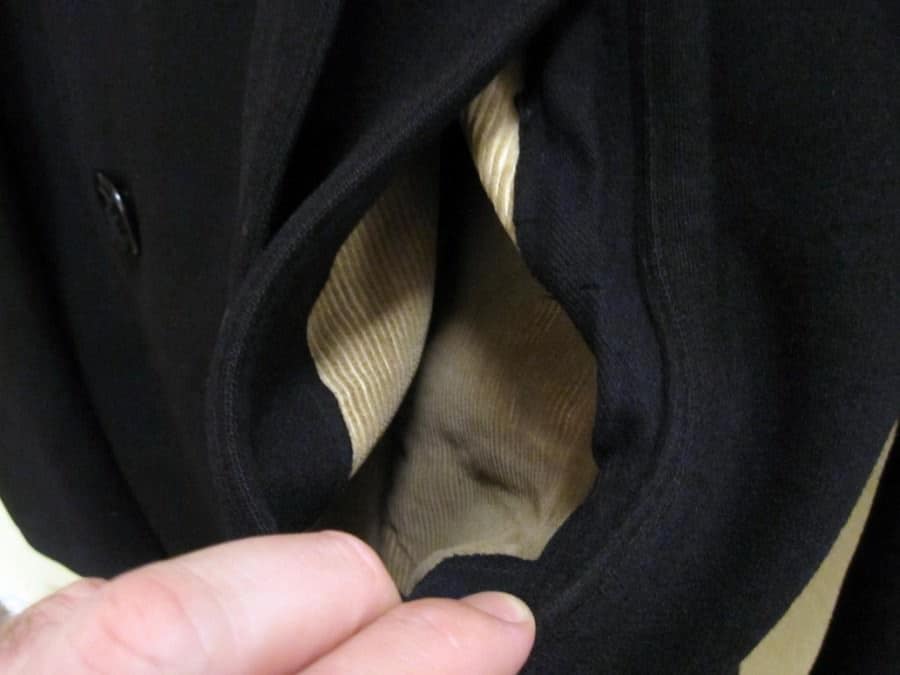

How to Date Your Vintage Peacoat
If you came into possession of a vintage peacoat and you wonder how old it is, or you just want to know when certain details like mid-brown corduroy lined pockets were available.
Peacoats From World War I
Peacoats have been around for longer, but it is difficult to find older pictures. As you can see the Peacoat had 10 or more buttons, and they were longer. It featured handwarmer pockets as well as flapped pockets. The original buttons featured an anchor with 13 stars around them, and the color was midnight blue. So it should be very easy to date a WWI peacoat if you find one.
Peacoats From World War II
Compared to the WWI peacoats, the hand warmer pockets were placed a bit lower, and the flap pockets disappeared, but it still maintained the 10 button front. The buttons changed considerably and now featured the fouled anchor you may be familiar with today. At the same time, the stars were removed.
The outer shell was still 100% midnight blue Kersey wool, and the pockets were lined with tan or light brown corduroy and inside the chest pocket you could find a label stating "Manufactured By NAVAL CLOTHING FACTORY."
The fit of WWII peacoats was very tight compared to the ones that followed.
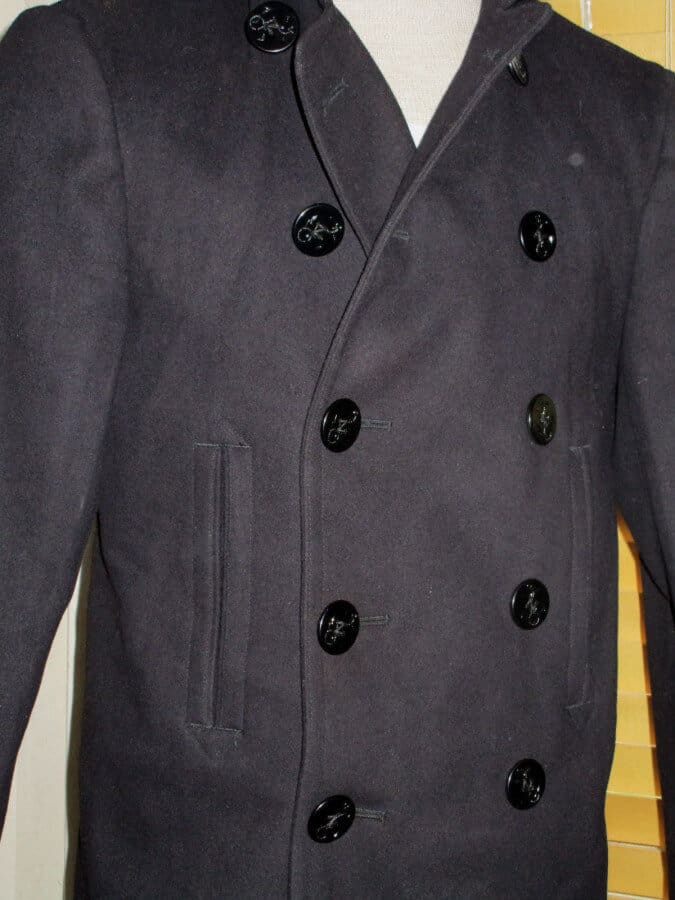

Peacoats Post-World War II
Traditionally, the peacoat had 10 buttons, 8 of which were visible. Sometime after the war the number was reduced to 8 with just 6 visible ones and eventually, just 7 with 6 visible ones.
Because of the reduction in buttons, the lapel got slightly bigger, and you could now see more of the chest or tie. Of course, you could still button it up all the way to keep you warm when needed. Up until the 1970s the 100%, Kersey wool remained unchanged. At some point after that, poly blended wool was offered. The style of the coat was maintained between 1946–1979, though the tags were often different, thus making it difficult to date.
However, little details changed. For example in 1968, the corduroy pocket lining was substituted with a soft blue, white, off-white cotton lining.
From 1974 to 1984 the buttons were exchanged once again, so the shape would match the gold bridge coats but the color was pewter. In 1984, the black fouled anchor button was reintroduced but the bridge coats kept their gold buttons.
During that same period, Melton was introduced along with some other changes.
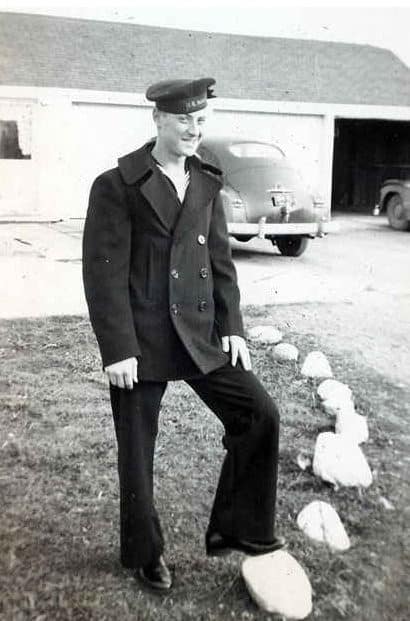

For even more details about dating a vintage peacoat, you should take a look here.
Conclusion
In the end, the peacoat is a classic, functional closet staple that has been around for more than three centuries. The original midnight blue version with black anchor buttons is certainly the most popular, but nowadays you do have a choice of different materials and colors. No matter whether you go vintage or new, a peacoat is ideal when you want to keep warm but a long overcoat would be too formal and a puffy down jacket à la Moncler is simply not your style.
Source: https://www.gentlemansgazette.com/peacoat-guide-history-sizing-buy/

0 Response to "Navy Blue Classic Peacoat Womans Wool Cracker Jack"
Post a Comment